![]()
S Jiang, L Liu, P Peng, M Xu, R Yan*
Prediction of vessel arrival time to port: a review of current studies
Maritime Policy & Management, 2025, 1-26
read the abstract
Accurate prediction of vessel arrival time is crucial for the efficiency of port operations and international trade; however, a systematic review of the research on this topic has not yet been conducted. This paper provides the first systematic review of the prediction of vessel arrival time to port, encompassing 29 academic studies published since 2011. By reviewing the literature, it first identifies and categorizes six key factors affecting vessel arrival time prediction: vessel static information, dynamic information, route conditions, environmental conditions, human factors, and external unexpected factors. The review highlights the challenges of precise vessel arrival time prediction. After closely examining the existing research studies, we found that two frameworks, namely non-trajectory-based prediction of vessel’s ETA to port and prediction of vessel’s ETA to port by path finding, and four categories of prediction models are commonly used: statistical models, machine learning models, deep learning models, and reinforcement learning models. This review also explores potential future research directions and serves as a critical resource for feature usage, model selection, the current research state, and future development directions for researchers, industry practitioners, and policymakers, advancing the understanding and application of data-driven prediction methodologies for improved maritime operational efficiency and digitalization.
HTMLARTICLE
![]()
Liang Zhao, Mengqiao Xu, Lei Liu, Yong Bai, Mingyang Zhang* & Ran Yan*
Intelligent shipping: integrating autonomous maneuvering and maritime knowledge in the Singapore-Rotterdam Corridor
Communications Engineering, 2025, 4:11
read the abstract
Designing safe and reliable routes is the core of intelligent shipping. However, existing methods for industrial use are inadequate, primarily due to the lack of considering company preferences and ship maneuvering characteristics. To address these challenges, here we introduce a methodological framework that integrates maritime knowledge and autonomous maneuvering model. Based on historical maritime big data, the framework offers customized routes for companies with specific routing preferences. The autonomous maneuvering model then evaluates the safety and reliability of the routes by considering ship motion characteristics and ocean hydrodynamics. We validate its effectiveness on the world’s longest Green and Digital Shipping Corridor between Singapore and Rotterdam. Results demonstrate that our model can provide customized route design for companies and enhance safety for shipping. The framework could serve as a fundamental structure to build a fully digitalized platform for route customization and evaluation for global shipping, optimizing operational decision-making and safety assurance.
HTMLARTICLE
![]()
Mengqiao Xu*, Yihui Shen, Yifan Zhu, Li Hong, Mengzhi Ma, Linyuan Lü*, Kevin X. Li*
Identification of critical sets of ports in cascading failures of global liner shipping network
Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review, 2025, 200: 104184
read the abstract
Cascading failures of port congestion propagation have become increasingly frequent in the global liner shipping network (GLSN), which harms international trade. To build resilience in maritime logistics, it is vital to proactively identify critical port sets whose initial failure would trigger severe consequences of port congestion propagation. This paper proposes a methodology for critical port sets identification in the cascading failures of GLSN, which integrates a cascading failure simulation model with a meta-heuristic optimization procedure. Specifically, a cascading failure model that considers liner shipping service routes’ port rotation adjustment behavior is introduced first. Then, the identification of critical port sets is formulated as a combinatorial optimization problem, seeking sets of ports whose simultaneous initial disruptions would trigger the largest cascade size; and an improved multi-population genetic algorithm is developed to solve this optimization problem. We demonstrate the usefulness of the proposed methodology by applying it to an empirical case of the GLSN, identifying the top 10 most critial sets of ports under different given values of set size. Extensive computational experiments validate the algorithm’s effectiveness in delivering high-quality solutions of approximate optimality. Results show that the critical sets of ports and their triggered cascade sizes are largely influenced by the service route behaviors of port rotation adjustments, and the influence becomes more profound with the increase in set size. Our proposed methodology serves as a valuable tool for proactively identifying worst-case scenarios of global port congestion propagation, thereby assisting stakeholders in resilient maritime logistics management.
HTMLARTICLE
![]()
Li Hong, Mengqiao Xu*, Yu Liu, Xuemei Zhang, Changjun Fan
A deep learning dismantling approach for understanding the structural vulnerability of complex networks
Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 2025, 194: 116148
read the abstract
Understanding the structural vulnerability of real-world complex networks is a crucial issue. This issue can be addressed by solving the so-called network dismantling problem, which aims to identify the smallest set of nodes for the fastest dismantling of a network. The network dismantling problem is a computationally challenging task due to its NP-hard nature. The powerful learning capabilities of machine learning methods provide a new perspective for solving this problem. Most existing deep learning methods are based on supervised learning, which rely on pre-labeled training data. These existing methods have achieved promising results in completely dismantling a network. However, they may not perform very well in identifying a very small number of nodes whose removal would significantly degrade—though far from fully dismantle—the network performance. This issue is particularly relevant to many real-world networks like transportation and infrastructure networks. This paper proposes a novel unsupervised learning model called GASC (Graph Attention network integrated with Shortcut Connections mechanism), to address this issue regarding the network dismantling problem. The GASC model employs the graph attention network to learn the underlying features of a network's topological structure and integrates the shortcut connections mechanism to overcome the vanishing gradients problem. Besides, we incorporate a network tailoring method to further improve the performance of our model. We performed comprehensive experiments on both synthetic networks and various real-world networks. The results validate that the proposed approach outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods and demonstrates significant robustness.
HTMLARTICLE
![]()
Li Hong, Yu Liu, Mengqiao Xu*, and Wenhui Deng
Combining deep reinforcement learning with heuristics to solve the traveling salesman problem
Chinese Physics B, 2025, 34(1): 018705
read the abstract
Recent studies employing deep learning to solve the traveling salesman problem (TSP) have mainly focused on learning construction heuristics. Such methods can improve TSP solutions, but still depend on additional programs. However, methods that focus on learning improvement heuristics to iteratively refine solutions remain insufficient. Traditional improvement heuristics are guided by a manually designed search strategy and may only achieve limited improvements. This paper proposes a novel framework for learning improvement heuristics, which automatically discovers better improvement policies for heuristics to iteratively solve the TSP. Our framework first designs a new architecture based on a transformer model to make the policy network parameterized, which introduces an action-dropout layer to prevent action selection from overfitting. It then proposes a deep reinforcement learning approach integrating a simulated annealing mechanism (named RL-SA) to learn the pairwise selected policy, aiming to improve the 2-opt algorithm's performance. The RL-SA leverages the whale optimization algorithm to generate initial solutions for better sampling efficiency and uses the Gaussian perturbation strategy to tackle the sparse reward problem of reinforcement learning. The experiment results show that the proposed approach is significantly superior to the state-of-the-art learning-based methods, and further reduces the gap between learning-based methods and highly optimized solvers in the benchmark datasets. Moreover, our pre-trained model M can be applied to guide the SA algorithm (named M-SA (ours)), which performs better than existing deep models in small-, medium-, and large-scale TSPLIB datasets. Additionally, the M-SA (ours) achieves excellent generalization performance in a real-world dataset on global liner shipping routes, with the optimization percentages in distance reduction ranging from 3.52% to 17.99%.
HTMLARTICLE
![]()
Tao Li, Yu Qin, Mengqiao Xu, Yanjie Zhou*, Lili Rong
Spatio-temporal vulnerability of high-speed rail line network in China
Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment, 2024(131): 104338
read the abstract
Previous literature mainly focuses on the vulnerability of high-speed rail network (HSRN) at station level. High-speed rail (HSR) lines fail frequently due to disasters, which can cause a cascading effect between lines. We propose a novel method to assess the vulnerability of HSR line network (HSRLN) from the spatio-temporal perspective. To do that, the lines are described by stations, and the relations between lines are defined by train scheduling data. Then, we use the passenger volume and travel time cost between lines to assess HSRLN’s vulnerability with disasters’ spatio-temporal characteristics. Finally, the HSRLN in China is taken as a case. When a disaster occurs at 11:00 and lasts 6 h or 9 h, it can cause a large vulnerability. The critical lines always cover the Beijing-Shanghai and Shanghai-Kunming lines, while the regions with high-level vulnerability are mainly distributed in the Yangtze River Delta.
HTMLARTICLE
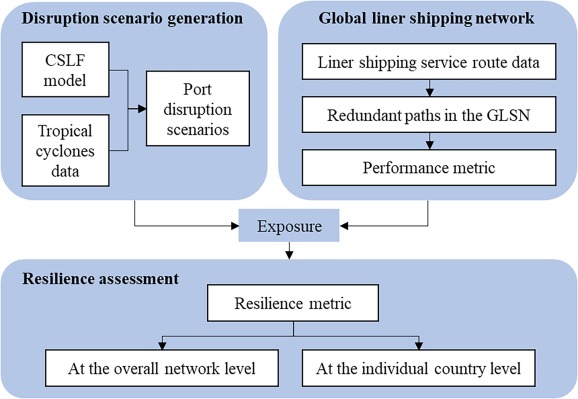
Mengqiao Xu*, Yifan Zhu, Kaishuo Liu, Adolf K. Y. Ng
Assessing resilience of global liner shipping network to tropical cyclones
Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment, 2024: 104189
阅读文章摘要
Tropical cyclones (TCs) are the primary natural disaster causing port disruptions, yet their impacts on global maritime transport remain largely unknown. This paper develops a framework to assess the resilience of global liner shipping network (GLSN) to TCs, focusing on path redundancy. The framework considers both direct and indirect impacts of port disruptions on GLSN performance in TC scenarios. We demonstrate this framework through case studies under historical and stress-test TC scenarios in the Western North Pacific region. Results show that the GLSN can be quite resilient in typical or mild-stress scenarios, but the increasing decline in its resilience under higher stress levels signals significant risks when facing with extreme scenarios. Those least resilient countries under mild stress turn out to be the same countries exhibiting least resilience under severe stress, most of which are SIDS countries. This research has implications for the design of resilient maritime transport networks.
HTMLARTICLE
Mengqiao Xu*, Wenhui Deng, Yifan Zhu, Linyuan LÜ*
Assessing and improving the structural robustness of global liner shipping system: A motif-based network science approach
Reliability Engineering and System Safety, 2023, 240: 109576
阅读文章摘要
Liner shipping carries about 70% of the total value of world's seaborne trade, and thus the robust functioning of global liner shipping network (GLSN) is essential for building robust global maritime logistics systems. However, understanding and improving the underlying structural robustness of GLSN is an important challenging topic. This paper contributes to this topic by proposing a motif-based network science approach to address two crucial tasks therein. First, based on the extensive mining of four-node motifs in the GLSN, we propose a novel node centrality metric named motif centrality to characterize the importance of a port in the GLSN, which proves its effectiveness in identifying critical ports for maintaining the GLSN structural robustness. Second, after assessing the GLSN structural robustness against some worst-case scenarios of port disruptions, we propose two motif-based link-adding strategies to improve the GLSN structural robustness. Experimental results prove their effectiveness as compared with random link-adding strategies. For further scrutinization, one strategy is extended to the individual country level and is found useful in improving the structural robustness of liner shipping connections of most countries, especially many underdeveloped maritime countries. Some practical and theoretical implications are finally discussed.
HTMLARTICLE
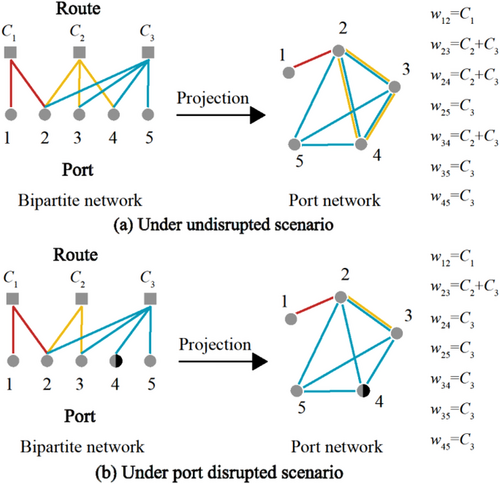
Xu, M.*, Zhu, Y., Deng, W., Shen Y., & Li, T*
Assessing the efficiency and vulnerability of global liner shipping network
Global Networks, 2023, 1–27
阅读文章摘要
Global liner shipping network (GLSN) constitutes an essential part of global maritime supply chains, but it could be vulnerable to disruptions. This paper develops an integrated framework for assessing the efficiency and vulnerability of GLSN. Specifically, a novel efficiency metric is proposed to quantify the performance of GLSN, and the framework enables modeling different levels of port disruption scenarios. Results show that the overall GLSN is quite robust under the partial disruption scenario of any single port (or of any single country's ports), but the damage to different countries is highly heterogeneous. Under dismantling scenarios where the identified most critical ports (countries) are successively disrupted, the GLSN vulnerability increases non-linearly with an increasing level of disruption. Our findings demonstrate that it is necessary to monitor and protect the identified critical ports (countries); especially, avoiding their simultaneously complete disruptions is of vital importance to the robust functionality of GLSN.
HTMLARTICLE
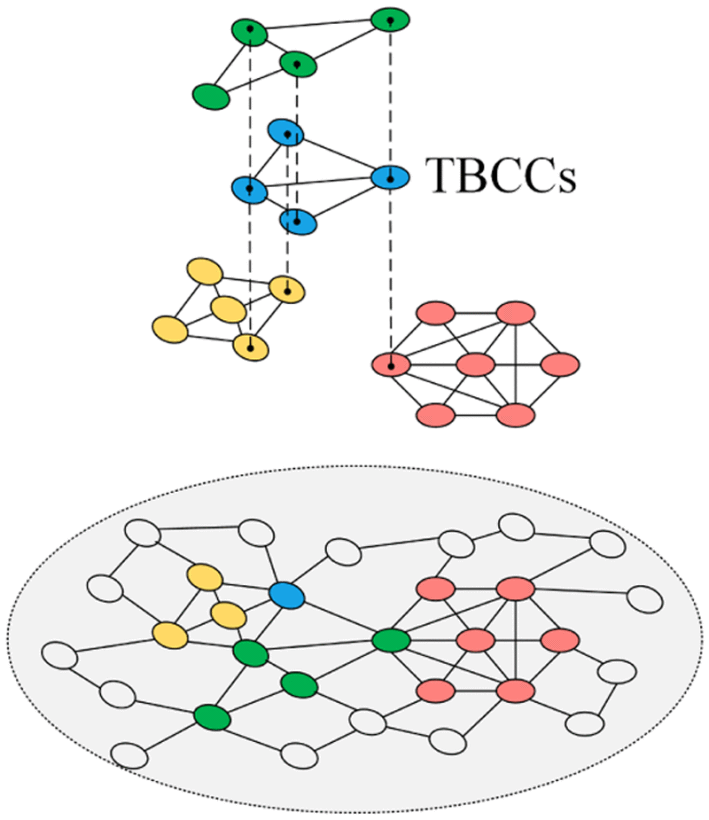
Xueming Liu, Yue Xu, Mengqiao Xu*, Wenhui Deng, Linqiang Pan, Adolf K. Y. Ng.
Two-Hop Biconnected Components in the Global Liner Shipping Network Reveal International Trade Statuses.
IEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering, 2023,10(3): 1564-1574
阅读文章摘要
Over 80% of global trade is carried by sea, and 70% of global seaborne trade by value is realized by liner shipping. The global liner shipping network (GLSN) is essential to facilitating international trade. To explore the transportation mechanism of the GLSN, we study a structure termed “two-hop biconnected component”(TBCC) which is a type of highly robust and efficient connected local structure. We find that TBCC is a salient structural property of the GLSN and is strongly associated with international trade statuses. Ports that appear more frequently in TBCCs tend to gain higher container throughputs in reality and play more important roles in maintaining the overall network robustness. Furthermore, we find that countries belonging to the same TBCCs tend to have closer trading relationships and form meaningful multilateral trade clusters in the future. The discovery of TBCC can help better understand international trade statuses and enable better design of robust and efficient liner shipping service routes.
HTMLARTICLE
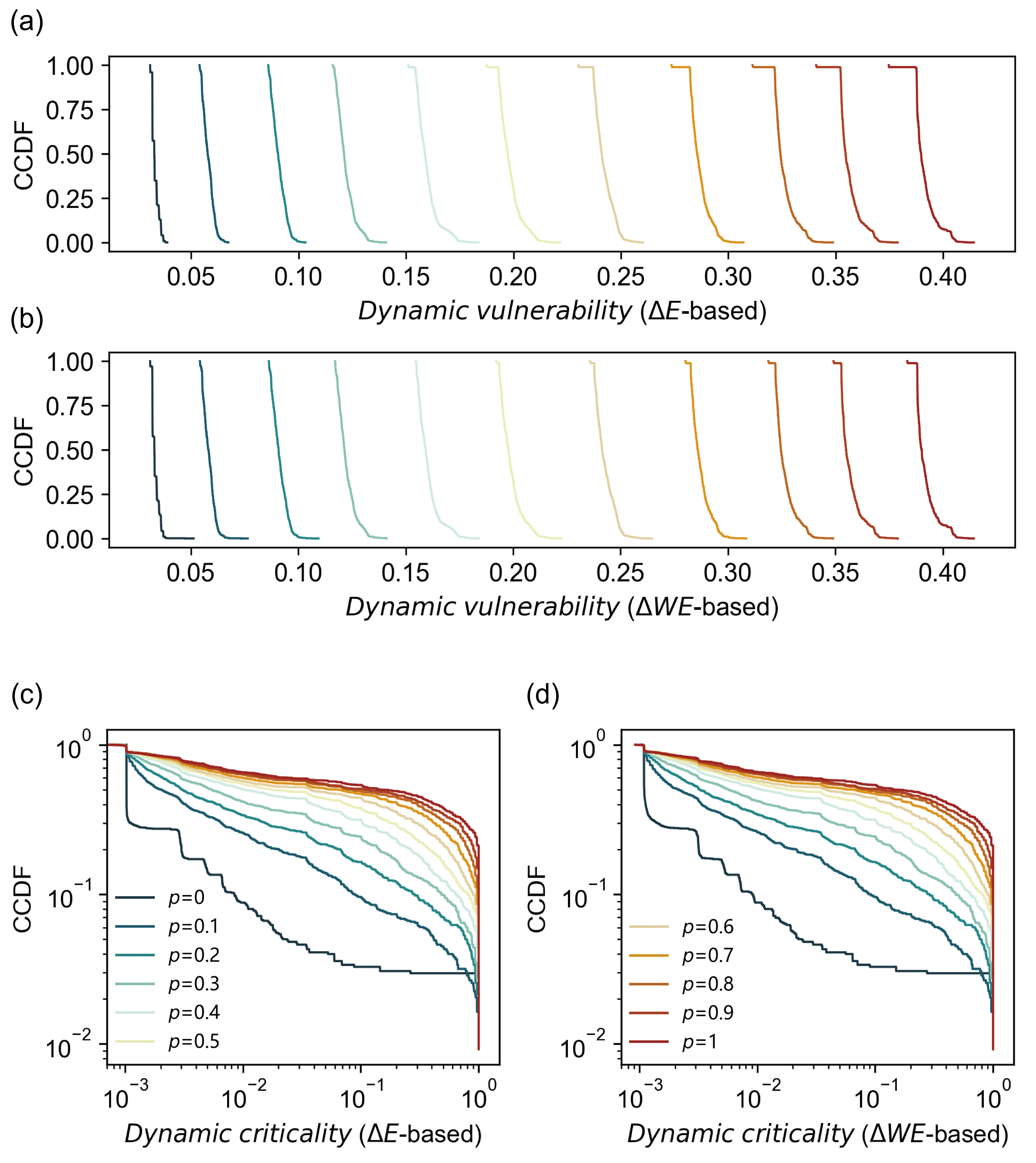
Xiujuan Xu, Yifan Zhu, Mengqiao Xu*, Wenhui Deng, Yuqing Zuo.
Vulnerability analysis of the global liner shipping network: from static structure to cascading failure dynamics.
Ocean and coastal management, 2022,
阅读文章摘要
Robust maritime transportation networks are essential to the development of world economy. But vulnerability of the global liner shipping network (GLSN) to unexpected interruptions has become apparent since the COVID-19 pandemic began, in that a single port interruption could be sufficient to trigger a cascading failure (i.e., port congestion propagation). To understand the vulnerability of the GLSN under such cascading failures, we propose a novel cascading model, which incorporates the realistic factor of liner shipping service routes’ behavior of port rotation adjustments under port failures. We apply the model to an empirical GLSN, showing that the GLSN under cascading failures is significantly more vulnerable than its static structure. Regarding two common adjustments of service routes’ port rotations (i.e., skipping failed ports and choosing alternative ports), we find that choosing alternative ports increases the GLSN vulnerability to cascading failures. Within the proposed model, we also introduce a metric termed port dynamic criticality to characterize the contribution of each port to the overall network robustness against cascading failures, finding it significantly and positively associated with port’s topological centrality in the initial GLSN. These findings provide managerial insights into preventing or mitigating port congestion propagation in the GLSN.
HTMLARTICLE
HTMLKEY RESULTS & VISUALIZATION
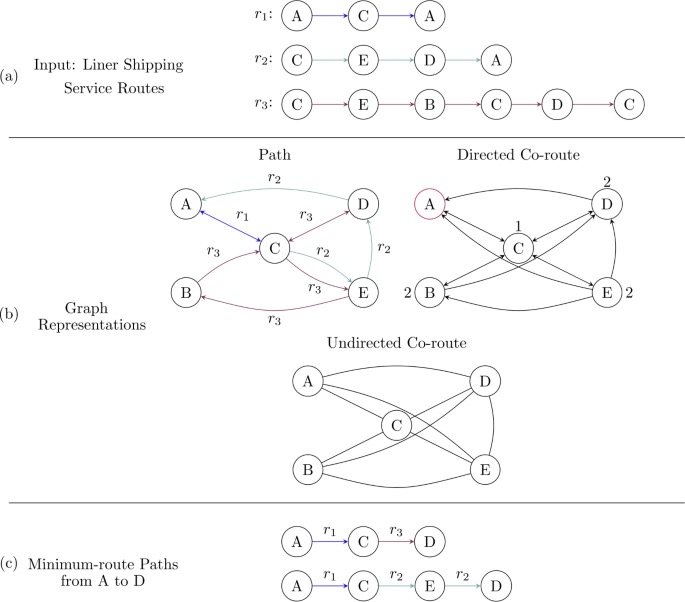
Timothy LaRock, Mengqiao Xu*, Tina Eliassi-Rad
A Path-based Approach to Analyzing the Global Liner Shipping Network
EPJ Data Science. 2022
阅读文章摘要
The maritime shipping network is the backbone of global trade. Data about the movement of cargo through this network comes in various forms, from ship-level Automatic Identification System (AIS) data, to aggregated bilateral trade volume statistics. Multiple network representations of the shipping system can be derived from any one data source, each of which has advantages and disadvantages. In this work, we examine data in the form of liner shipping service routes, a list of walks through the port-to-port network aggregated from individual shipping companies by a large shipping logistics database. This data is inherently sequential, in that each route represents a sequence of ports called upon by a cargo ship. Previous work has analyzed this data without taking full advantage of the sequential information. Our contribution is to develop a path-based methodology for analyzing liner shipping service route data, computing navigational trajectories through the network that respect the routes and comparing these paths with those computed using other network representations of the same data. We further use these trajectories to re-analyze the role of a previously-identified structural core through the network, as well as to define and analyze a measure of betweenness centrality for nodes and edges.
HTMLARTICLE
Mengqiao Xu , Qian Pan, Haoxiang Xia, Naoki Masuda*.
Estimating international trade statuses of individual countries from a global liner shipping network.
Royal Society Open Science, 2020, 7: 200386
阅读文章摘要
Maritime shipping is a backbone of international trade and, thus, the world economy. Cargo-loaded vessels travel from one country's port to another via an underlying port-to-port transport network, contributing to international trade values of countries en route. We hypothesize that ports that involve trans-shipment activities serve as a third-party broker to mediate trade between two foreign countries and contribute to the corresponding country's status in international trade. We test this hypothesis using a port-level dataset of global liner shipping services. We propose two indices that quantify the importance of countries in the global liner shipping network and show that they explain a large amount of variation in individual countries' international trade values and related measures. These results support a long-standing view in maritime economics, which has yet to be directly tested, that countries that are strongly integrated into the global maritime transportation network have enhanced access to global markets and trade opportunities.
HTMLARTICLE
HTMLCODE
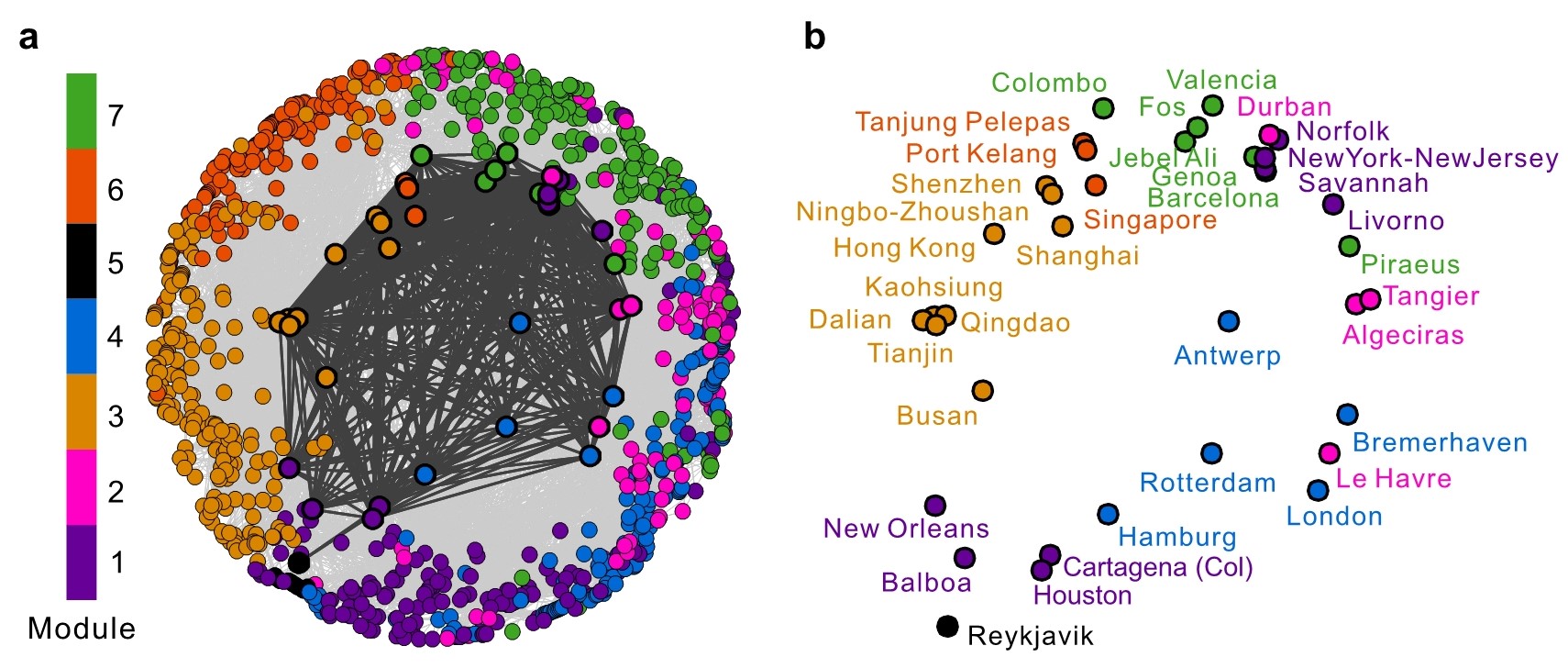
Mengqiao Xu# *, Qian Pan#, Alessandro Muscoloni, Haoxiang Xia*, Carlo Vittorio Cannistraci*.
Modular gateway-ness connectivity and structural core organization in maritime network science.
Nature Communications, 11, 2849 (2020)
阅读文章摘要
Around 80% of global trade by volume is transported by sea, and thus the maritime transportation
system is fundamental to the world economy. To better exploit new international shipping routes,
we need to understand the current ones and their complex systems association with international
trade. We investigate the structure of the global liner shipping network (GLSN), finding it is an
economic small-world network with a trade-off between high transportation efficiency and low
wiring cost. To enhance understanding of this trade-off, we examine the modular segregation of
the GLSN; we study provincial-, connector-hub ports and propose the definition of gateway-hub
ports, using three respective structural measures. The gateway-hub structural-core organization
seems a salient property of the GLSN, which proves importantly associated to network integration
and function in realizing the cargo transportation of international trade. This finding offers new
insights into the GLSN’s structural organization complexity and its relevance to international trade.
HTMLARTICLE
XLSXDATA
HTMLCODE

Sadamori Kojaku#, Mengqiao Xu #, Haoxiang Xia, Naoki Masuda*.
Multiscale core-periphery structure in a global liner shipping network.
Scientific Reports, 2019, 9(1): 404.
阅读文章摘要
Maritime transport accounts for a majority of trades in volume, of which 70% in value is carried by container ships that transit regular routes on fixed schedules in the ocean. In the present paper, we analyse a data set of global liner shipping as a network of ports. In particular, we construct the network of the ports as the one-mode projection of a bipartite network composed of ports and ship routes. Like other transportation networks, global liner shipping networks may have core-periphery structure, where a core and a periphery are groups of densely and sparsely interconnected nodes, respectively. Core-periphery structure may have practical implications for understanding the robustness, efficiency and uneven development of international transportation systems. We develop an algorithm to detect core-periphery pairs in a network, which allows one to find core and peripheral nodes on different scales and uses a configuration model that accounts for the fact that the network is obtained by the one-mode projection of a bipartite network. We also found that most ports are core (as opposed to peripheral) ports and that ports in some countries in Europe, America and Asia belong to a global core-periphery pair across different scales, whereas ports in other countries do not.
HTMLARTICLE
![]()
Mengqiao Xu*, Ling Zhang, Wen Li, Haoxiang Xia.
Mobility pattern of taxi passengers at intra-urban scale: empirical study of three cities.
Journal of Systems Science and Information, 2017, 5(6), 537-555.
阅读文章摘要
The study of human mobility patterns is of both theoretical and practical values in many aspects. For long-distance travel, a few research endeavors have shown that the displacements of human travels follow a power-law distribution. However, controversies remain regarding the issue of the scaling laws of human mobility in intra-urban areas. In this work, we focus on the mobility pattern of taxi passengers by examining five datasets of three metropolitans. Through statistical analysis, we find that the lognormal distribution with a power-law tail can best approximate both the displacement and the duration time of taxi trips in all the examined cities. The universality of the scaling laws of human mobility is subsequently discussed, in view of the analysis of the data. The consistency of the statistical properties of the selected datasets that cover different cities and study periods suggests that, the identified pattern of taxi-based intra-urban travels seems to be ubiquitous over cities and time periods.
HTMLARTICLE
Mengqiao Xu*, Haoxiang Xia.
Hub dependency and vulnerability of China's overseas connections. In: Cesar Ducruet (Ed.), Advances in Shipping Data Analysis and Modeling:
Tracking and Mapping Maritime Flows in the Age of Big Data, 2017. London: Routledge. (Book chapter)
arXiv preprint,arXiv preprint,arXiv preprint,arXiv preprint,arXiv preprint,dd
HTMLARTICLE
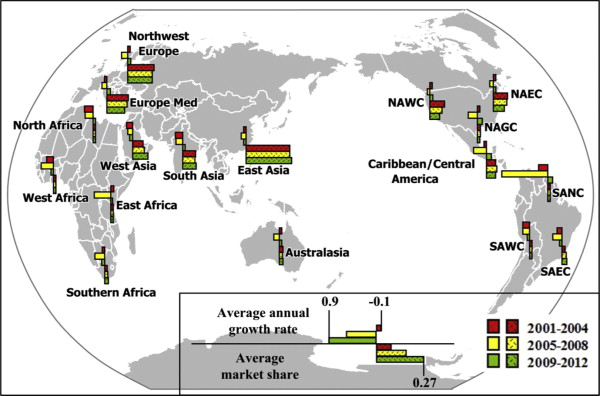
Mengqiao Xu*, Zhenfu Li, Yanlei Shi, Xiaoling Zhang, Shufei Jiang.
Evolution of regional inequality in the global shipping network.
Journal of Transport Geography, 2015, 44: 1-12.
阅读文章摘要
Global shipping is a backbone of the global economy, and as such, it evolves alongside the development of trade and the elaboration of commodity chains. This paper investigates the evolution of regional inequality in the global shipping network by analyzing the changing positions of world regions during the period from 2001 to 2012. This was a period of both prosperity and recession in maritime shipping. Using data on inter-regional flow connections, the positions of seventeen regions in the global shipping network are analyzed in terms of their traffic development, centrality, dominance and vulnerability. The East Asian, Northwest European and Europe Mediterranean regions have consistently held the highest positions, while East African and North African regions have held the lowest positions. By commanding the largest flows in the network, East Asia assumes a dominant position. The Australasian, North American West Coast, Northwest European and Southern African regions show an increasing dependency on East Asia. The analysis also identifies a few emerging regions that have had the highest growth rates in total traffic volume and connectivity for the studied period, namely South American North Coast, South American East Coast, West Africa, Southern Africa and West Asia. The empirical results of this paper supplement existing research on global shipping network evolution. One implication of the analysis is that the traffic growth of East Asia does not imply that, there is an equivalent improvement in its position in the global shipping network. The paper also shows that indicators from network analysis may be used to provide a more nuanced understanding of port-regional development than existing measures based solely on total traffic volume.
HTMLARTICLE
![]()
Zhenfu Li, Mengqiao Xu*, Yanlei Shi.
Centrality in global shipping network basing on worldwide shipping areas.
GeoJournal, 2015, 80(1): 47-60.
阅读文章摘要
Port and maritime studies dealing with containerization have observed close correlation between global liner shipping and world trade, and centrality in global shipping network (GSN) may change as the situation of world economy and trade changes. Meanwhile, the influence that shipping areas have on the GSN is much greater than any single port, and connections between these shipping areas affect the structure of the GSN. This paper wishes to understand the dynamic changing of the centrality in the GSN during the period from 2001 to 2012, which sees both booms and depressions in world economy and liner shipping. The paper divides global shipping into 25 areas from geographical perspective, and presents an analysis of each shipping area’s position in the GSN through indicators of centrality. The results reveal that to a large extent Europe is always in the center of the GSN from 2001 to 2012, but its central position is declining. Additionally, mapping the centrality distribution of those shipping areas in the latest year confirms their current positions in the GSN.
HTMLARTICLE
徐梦俏*, 李振福, 史砚磊, 张小玲, 姜书飞.
世界集装箱海运网络空间联系强度.
上海海事大学学报, 2015, 36(3): 6-12
阅读文章摘要
针对目前考虑海运节点真实地理分布的海运网络空间联系强度研究较为缺乏的事实,以及为衡量北极航线开通对世界集装箱海运网络空间联系强度的影响,以世界集装箱海运网络为例进行研究.阐述"世界集装箱海运网络空间联系强度"概念,并基于空间相互作用理论中的引力模型,提出两个节点之间的集装箱海运空间联系强度计算方法;对2004—2012年中国与北美洲、欧洲地区的17个主要海运国家的集装箱海运空间联系强度进行实证研究,分析北极航线对此的影响.结果表明,北极航线的开通将使中国与加拿大、美国及西北欧海运国家的集装箱海运空间联系强度增大.
HTMLARTICLE
李振福, 李婉莹, 徐梦俏.
新海上丝绸之路集装箱海运网络中心性.
中国航海, 2018, 41(3): 126-131, 137.
阅读文章摘要
在界定新海上丝绸之路核心区域的基础上,选取区域内34个主要集装箱港口,依据全球前20家航运公司的航线数据构建有向的新海上丝绸之路集装箱海运网络。采用度数中心度、特征向量中心度、接近中心度、中介中心度和流介中心度指标对港口的中心地位进行分析。结果显示,香港港、深圳港、大连港、新加坡港和上海港具有较高的地位,但多数丝路沿线港口的地位滞后于其在新海上丝绸之路建设中应具有的重要性。
HTMLARTICLE
李振福, 刘诗炎, 徐梦俏.
中国集装箱内河运输网络的结构脆弱性研究.
地域研究与开发, 2018, 37(3): 13-18.
阅读文章摘要
根据内河集装箱班轮运输航线的港口挂靠信息,构建中国集装箱内河运输网络。基于复杂网络理论中衡量节点重要性的度中心性和中介中心性指标,模拟针对港口的蓄意攻击,分析中国集装箱内河运输网络的结构脆弱性。结果表明:两种蓄意攻击下,当失效港口比例达到33%时,网络基本都陷入瘫痪;与基于港口度中心性攻击相比,网络结构应对港口中介中心性攻击时较为脆弱。此外,进一步结合港口的空间分布格局,识别出对于维持中国集装箱内河运输网络稳定起决定性作用的14个重要港口及其影响范围。
HTMLARTICLE
李振福, 梁爱梅, 徐梦俏.
我国北极社会科学研究的作者网络.
世界地理研究, 2018, 27(3): 33-44.
阅读文章摘要
北极社会科学研究是在北极权益博弈日益激烈的背景下逐渐发展起来的新兴科研领域,对研究领域的合著网络及引用网络进行分析有助于了解作者间的关系模式及知识流动的特点。以2007年~2015年北极社会科学研究中文期刊文献为基础,采用中心性分析、社团分析对北极社会科学研究的合著网络和引用网络进行了结构分析。结果表明,当前我国北极社会科学研究者之间已初步形成多个规模较大的团体,但绝大部分研究者较为分散,沟通合作机制缺乏;此外,活跃作者之间的信息流动具有明显的不对称性,代际特征开始凸显。应激发不同领域人员参与北极社会科学研究的积极性,引导其形成优势互补的研究团队,推动北极社会科学研究的发展。
HTMLARTICLE
李振福, 史砚磊, 徐梦俏, 张小玲, 姜书飞.
世界集装箱海运网络层次结构研究.
系统工程理论与实践, 2016, 36(4): 981-988
阅读文章摘要
将世界集装箱班轮运输划分为18个海运区域,根据17家主要班轮公司593个港口的航线连接数据统计18个海运区域间的航线连接情况,构建以连接频率为权重的加权世界集装箱海运网络.结合优势流分析和显著流分析对海运网络的层次结构进行研究,结果表明世界集装箱海运网络具有明显的层次性,可分为四层.各层次区域之间存在海运联系且不同层次的区域在网络中具有不同的作用,第一层次海运区域处于核心地位,第二层次及第三层次的部分海运区域的中介性较强.在此基础上,进一步探讨东亚和西北欧两个核心区域与其他区域的相对海运距离,分析海运区域间的内在联系.
HTMLARTICLE
李振福, 史砚磊, 徐梦俏, 张小玲.
亚洲集装箱港口的全球班轮网络地位.
经济地理, 2016, 36(3): 91-98.
阅读文章摘要
运用复杂网络理论中节点重要性的分析方法,从班轮公司全球海运服务网络的角度对亚洲集装箱港口的地位进行评估。通过对中远集运和马士基全球班轮海运服务网络中港口节点的度、点强度和特征向量指标计算,发现上海、新加坡、深圳、宁波、香港和釜山几个亚洲港口在两个网络中都具有很高的地位;同时,广州、天津、大连等中国港口存在较大的发展潜力。最后,为中国港口的发展提出了建议。
HTMLARTICLE
李振福,姜书飞, 徐梦俏, 史砚磊, 张小玲.
面向北极航线通航的海运网络演化研究.
复杂系统与复杂性科学, 2015, 12(4):55-60
阅读文章摘要
基于复杂网络理论,构建以港口间海运距离和吸引度为基础的复杂网络演化模型。选取全球25个主要集装箱港口2010年相关数据,对比演化网络、实际网络和同等规模的随机网络,验证了模型的有效性。将模型应用于北极航线通航后的海运网络,结果显示,北极航线通航后海运网络平均路径长度减小,表明北极航线开通加强了港口间的联系;部分东北亚及西北欧港口度值增加较为明显;港口核度更趋于极化,表明北极航线增强了海运网络的层次性。
HTMLARTICLE
李振福, 张小玲, 徐梦俏, 史砚磊, 姜书飞.
东亚集装箱港口体系层次结构.
系统工程, 2015,33(12):78-84.
阅读文章摘要
在确定33个东亚集装箱港口的基础上,根据全球运力份额前20名班轮公司的现有航线分布情况,构建了一个港口的有向二分网络。运用复杂网络中的k-核分析对该港口网络进行层次划分,分析各个层次内部和层次之间港口的连接关系并考察了低层次港口的k-核深度。此外还分析了核心结构的小世界特性,并分别从聚集系数、平均最短路径长度以及接近中心势三个方面,针对最高层次中的每个港口对网络整体结构的影响进行了进一步研究。
HTMLARTICLE
李振福, 张小玲, 徐梦俏, 史砚磊.
东亚集装箱港口体系集装箱化进程研究.
北京交通大学学报, 2015, 39(3): 48-55.
阅读文章摘要
在确定50个东亚港口的基础上,按照这些港口在1993—2013年的集装箱吞吐量增长模式,结合康德拉捷夫长波对东亚集装箱港口体系的集装箱化过程进行研究,结果表明从1993年以来经历了三个发展阶段.在此基础上,将每个阶段包含的港口视为一个港口群,运用基尼系数分解法对东亚集装箱港口体系的不平衡性进行深入分析.分析显示,东亚集装箱港口体系的不平衡性从主要受港口群之间吞吐量的不平衡性的影响,逐渐转移到受重叠部分的影响,即传统优势枢纽港的发展相对停滞,而以上海港、深圳港为代表的新枢纽港的强势崛起是造成不平衡性的主要原因.
HTMLARTICLE
李振福, 王文雅, 徐梦俏.
基于PT理论的中国北极航线权益战略选择.
世界地理研究, 2015, 24(3): 50-58.
阅读文章摘要
面对北极航线的开通预期,世界各相关国家对北极航线问题愈加关注,但目前我国国内缺乏对于中国北极航线战略的量化研究,在全面分析目前中国北极航线的内部优势、劣势及外部环境的基础上,利用PT理论创建了中国北极航线权益战略PT理论选择方法,并通过方案选择提出了中国北极航线权益战略。研究结果对于北极及北极航线研究领域中环境因素的分析和量化方法的拓展及制定我国北极航线战略具有理论和现实意义。
HTMLARTICLE
李振福, 李贺, 徐梦俏, 史砚磊.
世界海运网络可达性对比研究.
大连海事大学学报, 2014, 40(1): 101-104.
阅读文章摘要
为深入研究北极航线在世界海运网络发展中的作用,借助原有的重力模型,提出一种更适于研究世界海运网络可达性的改进的重力模型.通过苏伊士运河、巴拿马运河以及北极航线对世界海运网络可达性的影响对比研究可知,北极航线的全线开通将为世界海运网络带来前所未有的巨大变革.该文旨在为更进一步研究世界海运网络演变提供基础.
HTMLARTICLE
李振福, 李贺, 徐梦俏, 李漪.
世界海运网络演变及未来发展趋势研究.
太平洋学报, 2014, 22(5): 95-105.
阅读文章摘要
世界海运网络从零星的贸易路线到遍布全球的贸易网络的形成,经历了长达5000多年的时间,其发展历程可分为四个阶段:初现期、均衡发展期、剧变期及平稳发展期。本文以1763年为重要分界线,从地理位置、资源优势、政治状况、航海技术、供需定律、航运中心的形成等六个方面,分析了世界海运网络的演变过程,进而对世界海运网络的演变趋势进行了分析和预测,认为亚太地区有望成为新的航运中心。作为主要海运大国的中国,更应当采取积极的发展策略,应对世界海运网络演变所带来的巨大变革。
HTMLARTICLE










